| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 커머스
- Go-lang
- study
- AWS 비용 절감
- AWS
- leetcode
- 지표
- 14일 공부
- Til
- 실용주의 프로그래머
- DevOps
- ssh
- PostgreSQL
- 경로 계획 알고리즘
- amazon ecs
- 신혼 여행
- 논문 정리
- 회고
- github
- Playwright
- Rust
- 디자인 패턴
- 생성 패턴
- docker
- 청첩장 모임
- 구조 패턴
- 오블완
- terraform
- 티스토리챌린지
- MAPF
- Today
- Total
밤 늦게까지 여는 카페
[leetcode] 75. Sort Colors - 이번에는 Runtime 100% 찍었습니다! 본문
안녕하세요. 이번에는 leetcode의 75. Sort Colors 문제를 풀어봤습니다.
놀랍게도 첫 시도에 runtime 100%를 찍을 수 있었는데요.

한번 정리해보겠습니다!
1. 문제
이 문제에서는 길이 n인 수열이 주어집니다. 수열은 0, 1, 2로 이뤄져있고 0은 빨간색, 1은 하얀색, 2는 파란색을 의미합니다.
라이브러리 사용 없이 수열을 0, 1, 2 순으로 정렬해야 합니다.
+ 새로운 수열을 반환하는 것이 아니라 수열 내부의 값을 바꿔줘야 합니다.
예시)
주어진 수열 [1, 0, 2, 1, 2, 2]을 [0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2] 로 바꿔야 합니다.
2. 풀이
제가 생각한 방법은
1. 수열을 앞에서부터 쭈욱 읽으면서
2. 순서가 잘못된(작은 수가 큰 수보다 뒤에 있는) 것을 발견하면
3. 바꿔주는 것입니다.
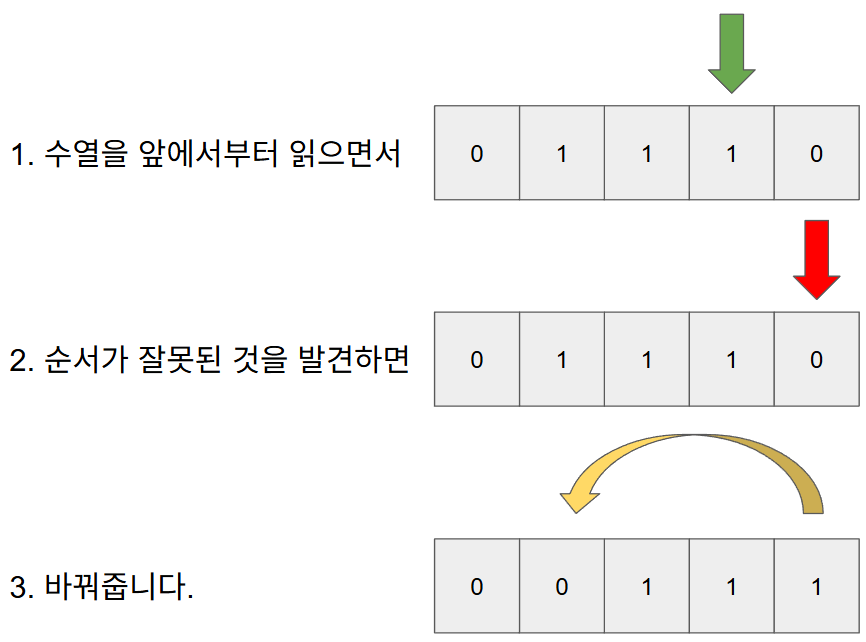
매우 간단한 접근법이지만 문제가 있습니다.
Q1. 3에서 순서를 바꿔줄 때 작은 수가 가야 할 위치를 어떻게 알 수 있을까요?
각 숫자들의 위치를 저장하면 됩니다.
1의 위치들을 저장해두었다가 0이 뒤에서 발견되었을 때 가장 앞에 있는 1의 위치와 바꿔주면 됩니다.
그러면 다음 질문이 따라옵니다.
Q2. 모든 위치를 전부 외우고 있어야 하는 것일까요?
우리는 0, 1, 2가 처음으로 발견되었던 위치만 기억하면 됩니다. 그리고 3에서 순서를 바꿔줄 때 큰 수의 첫 위치를 1만 증가시켜주면 됩니다.
pseudo code는 다음과 같습니다.
1. IDX=0, first_index_of_colors = [None, None, None]
2. Read the color in IDX
3. If it's the first occurence of the color, store IDX in first_index_of_colors[color]
4. Check that bigger color's first index is coming faster using first_index_of_colors
4.1. If there is no bigger color, INCREASE IDX
4.2. If there is a bigger color, change the order
5. repeat 2-4 till IDX becomes bigger than len(nums)
이 방법 이외에도 Counting Sort, Dutch Flag라는 유명한 방법들이 있던데 한번 공부해보시면 좋을 것 같습니다 :)
+코드
class Solution:
def sortColors(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
first_idx_of_colors = [None, None, None]
idx = 0
while idx < len(nums):
color = nums[idx]
if first_idx_of_colors[color] == None:
first_idx_of_colors[color] = idx
unordered_index = self.find_unordered_color(first_idx_of_colors, color, idx)
if unordered_index == -1:
idx += 1
continue
first_idx_of_colors[nums[unordered_index]] += 1
first_idx_of_colors[color] = min(unordered_index, first_idx_of_colors[color])
nums[unordered_index], nums[idx] = nums[idx], nums[unordered_index]
def find_unordered_color(self, first_idx_of_colors:List[int], color: int, index: int) -> int:
for i in range(color+1, len(first_idx_of_colors)):
first_idx_of_color = first_idx_of_colors[i]
if first_idx_of_color == None:
continue
if first_idx_of_color < index:
return first_idx_of_color
return -1
'알고리즘 > 문제풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 사칙 연산 계산 프로그램 구현하기 feat. Shunting Yard 알고리즘 (6) | 2025.07.22 |
|---|---|
| [leetcode] 399. Evaluate Division - 이번에도 Runtime 100%! (0) | 2025.06.03 |
| [leetcode] 2257. Count Unguarded Cells in the Grid #3 (2) | 2024.11.29 |
| [leetcode] 2257. Count Unguarded Cells in the Grid #2 (1) | 2024.11.27 |
| [leetcode] 2257. Count Unguarded Cells in the Grid (1) | 2024.11.23 |




