| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 청첩장 모임
- 구조 패턴
- 도커 주의사항
- 생성 패턴
- study
- Playwright
- Rust
- AWS
- 지표
- docker
- 14일 공부
- leetcode
- amazon ecs
- Go-lang
- AWS 비용 절감
- MAPF
- 티스토리챌린지
- Monthly Checklist
- 디자인 패턴
- Til
- DevOps
- 논문 정리
- ssh
- 신혼 여행
- 실용주의 프로그래머
- github
- 경로 계획 알고리즘
- terraform
- PostgreSQL
- 오블완
- Today
- Total
밤 늦게까지 여는 카페
WA* 알고리즘 - Heuristic 함수에 장난을 좀 쳐볼까요? 본문
안녕하세요. 오늘은 A* 알고리즘의 변형 중 하나인 Weighted A*(WA*) 알고리즘을 공부해보려고 해요!
- POHL, Ira. First results on the effect of error in heuristic search. Machine Intelligence, 1970, 5: 219-236.
- 이 논문을 보고 싶었는데 오래된 자료라서 찾지 못했네요 ㅜ
WA* 알고리즘은 제목에서 설명했던 것처럼 Heuristic 함수에 Weight 계수를 곱하는 것입니다.
이 간단한 조작이 어떤 영향을 주게 되는지 살펴볼까요?
1. WA* 알고리즘
기본적으로 A* 알고리즘과 동일하게 동작하지만 평가함수 f `이 다릅니다.
f ` = g ` + w * h ` (w >= 1)
- 시작 노드 s를 OPEN에 추가하고 평가 함수 f `(n)을 이용해서 f ` 값을 계산합니다.
- OPEN에서 f ` 값이 가장 작은 노드 n을 추출합니다.
- f ` 값이 최소인 노드들이 있다면 랜덤하게 아무 노드나 선택합니다.
- 하지만 G에 포함된 노드가 있다면 해당 노드를 먼저 고릅니다.
- 만약 선택된 노드 n이 G에 포함된다면 알고리즘을 종료합니다.
- 선택된 노드 n이 G에 포함되지 않는다면 n을 CLOSED에 추가합니다.
- Connected(n)들의 f `값을 계산합니다.
- Connected(n)들 중에서 CLOSED에 포함되어 있지 않은 노드들을 OPEN에 추가합니다.
- 이미 CLOSED에 포함되어 있는 경우, 새롭게 계산된 f `값이 기계산된 f `값보다 작을 경우에만 CLOSED에서 추출하고, OPEN에 추가합니다.
- 2로 돌아갑니다.
1보다 큰 w를 h `함수에 곱하는 것이 어떤 영향을 주게 될까요?
맨하튼 거리를 예시로 들어보면 GOAL 노드에 가까운 노드들을 먼저 탐색하게 됩니다.
"GOAL 노드에 가까운 노드들을 먼저 탐색하게 되면 좋은 것 아닌가?" 라고 생각할 수 있지만 경유지 하나 하나는 GOAL 노드와 가깝지만 전체 경로가 길어지는 문제가 생길 수 있습니다.
w 값이 커질수록 greedy 알고리즘과 비슷해지는 문제가 생기는 것이죠!
한번 예제 코드와 예시를 통해서 살펴볼까요?
2. 예제 코드
지금까지는 heuristic 함수를 h ` = 0 으로 설정했었지만 이번부터는 맨하튼 거리로 구현했습니다.
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List
import heapq
import copy
@dataclass
class Node:
id: int
x: float
y: float
g_val: float = 0
f_val: float = float("inf")
parent_id: int = None
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.f_val < other.f_val
@dataclass
class Edge:
start_node: Node
end_node: Node
weight: float
def get_other_node(self, node_id: int) -> Node:
if self.start_node.id == node_id:
return self.end_node
else:
return self.start_node
@dataclass
class Graph:
nodes: dict
adjacent_edges: dict
def get_node(self, node_id: int) -> Node:
return self.nodes[node_id]
def get_connected_nodes(self, node_id: int) -> List[Node]:
adjacent_edges = self.adjacent_edges.get(node_id, [])
return [edge.get_other_node(node_id) for edge in adjacent_edges]
def get_adjacent_edges(self, node_id: int) -> List[Edge]:
return self.adjacent_edges.get(node_id, [])
def set_edge_weight(self, edge_id: int, weight: float):
self.edges[edge_id].set_weight(weight)
def trace(self, node_id):
parent_id = self.nodes[node_id].parent_id
if parent_id != None:
return self.trace(parent_id) + [node_id]
return [node_id]
def wa(graph, start_node_id, end_node_id, W=1):
open_heap = []
open_dict = {}
closed_dict = {}
global num_of_expanded_open_list, num_of_maximum_expanded_node
num_of_expanded_open_list = 0
num_of_maximum_expanded_node = 0
def add_open(node_id):
heapq.heappush(open_heap, graph.get_node(node_id))
try:
open_dict[node_id] += 1
except:
open_dict[node_id] = 1
global num_of_expanded_open_list, num_of_maximum_expanded_node
num_of_expanded_open_list += 1
num_of_maximum_expanded_node = max(len(open_dict), num_of_maximum_expanded_node)
def pop_open():
node = heapq.heappop(open_heap)
open_dict[node.id] -= 1
if open_dict[node.id] < 0:
print("뭔가 잘못되었습니다!")
return node.id
def add_close(node_id):
closed_dict[node_id] = True
def remove_close(node_id):
del closed_dict[node_id]
end_node = graph.get_node(end_node_id)
def heuristic(node) -> float:
distance = abs(end_node.x - node.x) + abs(end_node.y - node.y)
return W * distance
start_node = graph.get_node(start_node_id)
start_node.g_val = 0
start_node.f_val = start_node.g_val + heuristic(start_node)
add_open(start_node_id)
while len(open_heap) > 0:
node = graph.get_node(pop_open())
if node.id == end_node_id:
break
add_close(node.id)
edges = graph.get_adjacent_edges(node.id)
for edge in edges:
other_node = edge.get_other_node(node.id)
new_f_val = node.g_val + edge.weight + heuristic(other_node)
if other_node.f_val == float("inf"):
other_node.g_val = node.g_val + edge.weight
other_node.f_val = new_f_val
if other_node.id not in closed_dict:
other_node.parent_id = node.id
add_open(other_node.id)
elif other_node.f_val > new_f_val:
other_node.parent_id = node.id
other_node.g_val = node.g_val + edge.weight
other_node.f_val = new_f_val
remove_close(other_node.id)
add_open(other_node.id)
print("W 값:", W)
print("최단 경로:", graph.trace(end_node_id))
print("실제로 탐색된 노드 수:", num_of_expanded_open_list)
print("OPEN 리스트에 저장되는 노드 개수의 최대값:", num_of_maximum_expanded_node)
print("====================")
def make_graph(grid: List[List[int]]) -> Graph:
nodes = {}
for rowIdx in range(len(grid)):
for colIdx in range(len(grid[rowIdx])):
if grid[rowIdx][colIdx] == 1:
continue
id = f"{colIdx}_{rowIdx*2}"
nodes[id] = Node(id=id, x=colIdx, y=rowIdx * 2)
adjacent_edges = {}
for rowIdx in range(len(grid)):
for colIdx in range(len(grid[rowIdx])):
if grid[rowIdx][colIdx] == 1:
continue
id = f"{colIdx}_{rowIdx*2}"
upper_id = f"{colIdx}_{rowIdx*2-2}"
lower_id = f"{colIdx}_{rowIdx*2+2}"
left_id = f"{colIdx-1}_{rowIdx*2}"
right_id = f"{colIdx+1}_{rowIdx*2}"
adjacent_edges[id] = []
try:
adjacent_edges[id].append(Edge(start_node=nodes[id], end_node=nodes[upper_id], weight=2))
except:
pass
try:
adjacent_edges[id].append(Edge(start_node=nodes[id], end_node=nodes[lower_id], weight=2))
except:
pass
try:
adjacent_edges[id].append(Edge(start_node=nodes[id], end_node=nodes[left_id], weight=1))
except:
pass
try:
adjacent_edges[id].append(Edge(start_node=nodes[id], end_node=nodes[right_id], weight=1))
except:
pass
return Graph(nodes=nodes, adjacent_edges=adjacent_edges)
if __name__ == "__main__":
grid = [
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
]
for val in range(4):
graph = make_graph(grid)
wa(graph, "0_0", "9_8", W=val)3. 예시
이번에는 격자 지도를 준비했습니다! (회색 격자는 갈 수 있는 곳, 검은 색 격자는 갈 수 없는 곳입니다)
- 의도대로 경로를 계획시키기 위해서 가로축 격자 간의 거리는 1이고 세로축 격자 간의 거리는 2입니다.
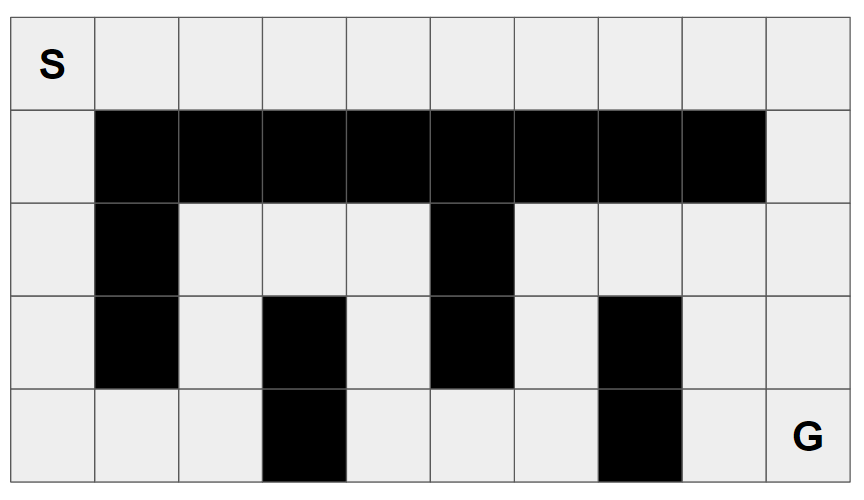

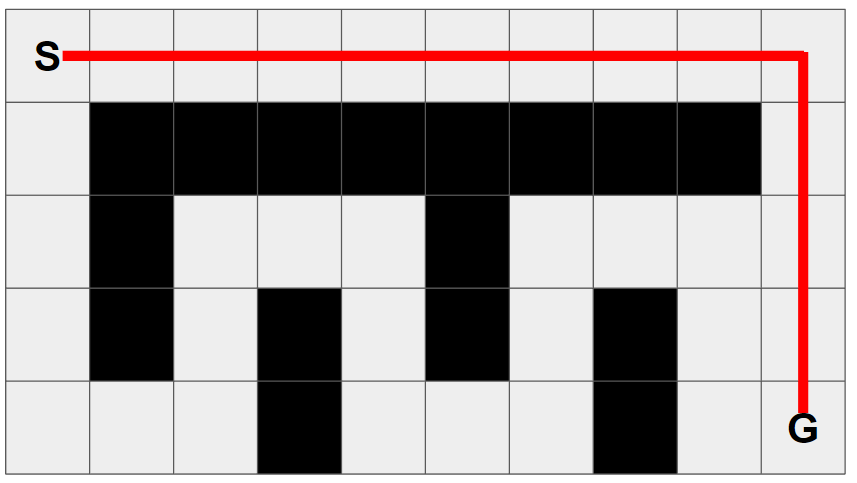
시작 노드는 S, 목적지 노드는 G 입니다.
- S = (0, 0), G = (9, 8)
원래 최단 경로는 아래 그림과 같습니다.
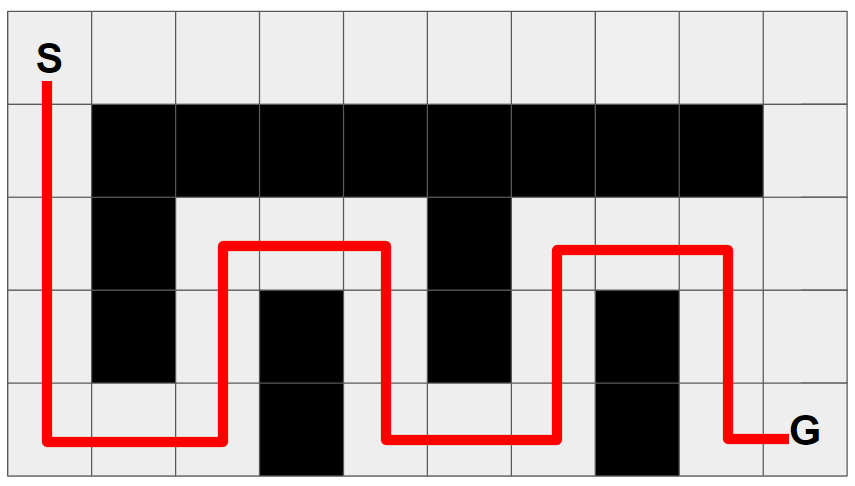
하지만 WA*는 W 값에 따라서 다음과 같은 경로를 찾게 될 수 있죠...
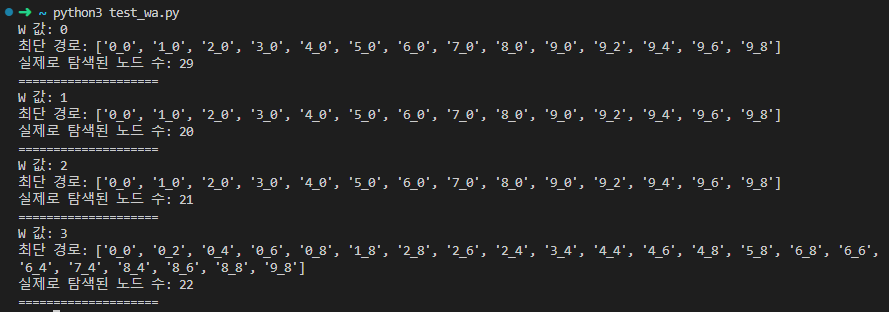
실제로 위의 예제 코드를 실행해보면 다음 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
- W=3 부터 비효율적인 경로를 반환하게 되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다 ㅜㅠ
WA* 알고리즘은 어떠셨나요? 간단하죠?
저는 W를 잘 정하는 방법에 대해서 궁금해지기 시작했습니다.
다행히도 Anytime A*에서 바로 이 내용을 다루더라고요!
WA* 알고리즘은 Anytime A*를 공부하기 위한 중간 단계로 생각하시면 될 것 같습니다 ㅎㅎㅎ
다음에는 Anytime A*를 정리해보도록 하겠습니다!
'알고리즘 > Path Finding' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스 알고리즘] 조이스틱 문제 - A* 알고리즘은 옳습니다. 틀린 건 저에요. (0) | 2023.05.20 |
|---|---|
| ARA* 알고리즘 - 처음부터 완벽할 필요는 없잖아요! (0) | 2023.05.08 |
| PEA* 알고리즘 - 이렇게 간단하다구요? 그럼에도 메모리 효율적이라구요? (0) | 2023.04.30 |
| IDA* 알고리즘 - A* 변형은 끝이 없는 것 같습니다. (0) | 2023.04.16 |
| SMA* 알고리즘 - 메모리를 고려한 A* 알고리즘의 변형이 또 있네요! (0) | 2023.04.14 |



